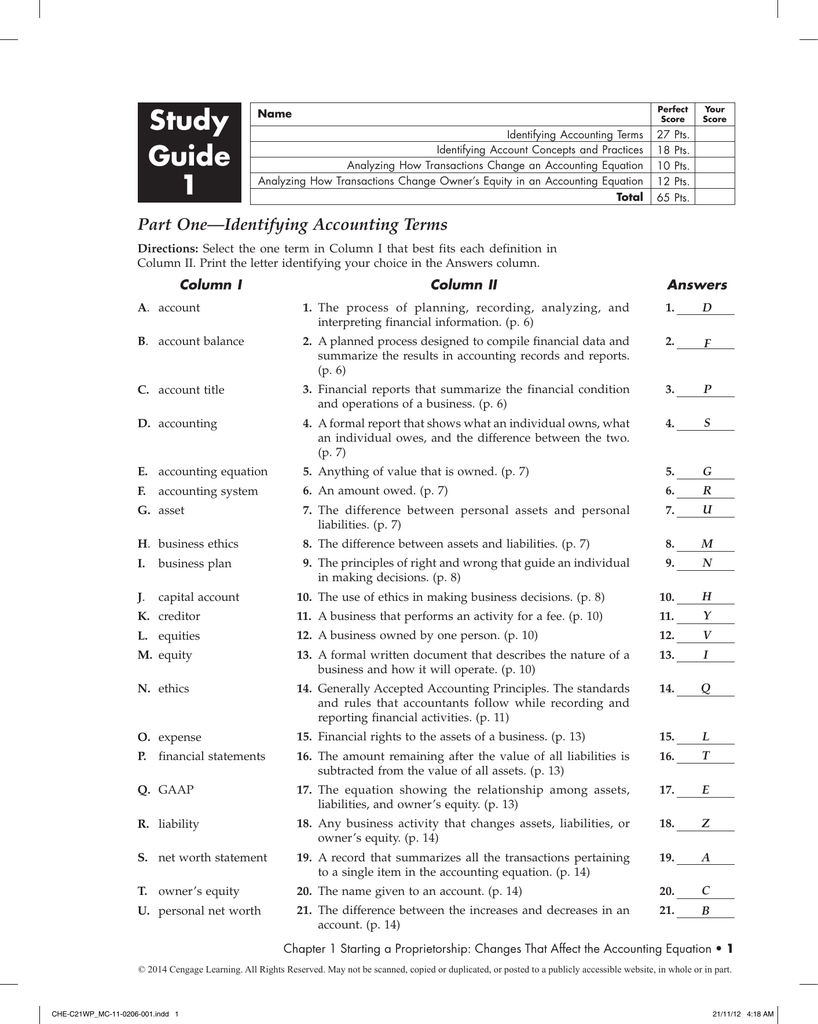
Chapter One Study Guide Accounting
One of the most important aspects of cost accounting is the preparation of reports that can be used by management in planning and controlling operations. Planning is the process of establishing goals and objectives and determining the means by which they will be met.
Total assets – total liabilities why? Because the assets of business are claimed by ether creditors or stockholders. To find out what belongs to stockholders, we subtract creditors’ claims (the liabilities) from the assets. Their remainder is the stockholders’ claim on the assets–stockholders’ equity. Often referred to as residual equity–that is, the equity “left over” after creditors claims are satisfied. The stockholders’ equity section of a corporation’s balance sheet generally consists of (1) common stock (2) retained earnings.
Financial Accounting Chapter 1: “Uses of Accounting Information and the Financial Statements” Accounting as an information system Accounting is an information system that measures, processes and communicates the financial information about a certain economic entity. An economic entity can be a business, hospital or a governmental body. The accountant of this economic entity focus on the needs of decision makers who use financial information, whether this decision makers are inside or outside of this company or operate in another economic entity.
Accountants provide vital service by supplying the information decision makers need to make “reasoned choices among alternative uses of scare resources in the conduct of business and economic activities.” 1. Accounting measures the business activities by recording the data about their compay for in the future.
The data that is gathered is saved until the company needs it and is then processed so that it can become useful information. All the information gathered is communicated through reports to all the decision makers. Business Goals, Activities and Performance Measures A business is an economic unit that has as aim to sell goods and services to their customers at prices that can be able to provide an adequate return to the owners of the company. Business Goals Profitability Business Activities Financing Operating Investing Liquidity Companies have different business activities but at the end they all have similar goals and engage in similar activities. The two major goals of the company are liquidity and Profitability.
→Profitability: This is the ability to earn enough income to attract and hold an investment capital. →Liquidity: Liquidity is the ability to have enough cash to pay debts when they are due.Example: A company may sell the necessary products to meet their goal of profitability but if their customers do not pay for their purchase quickly the company may not make enough money to pay their suppliers. If this happens the company fails to meet their liquidity. →Operating Activities: This includes selling goods and services to customers, employing managers and workers, buying and producing goods/services and paying taxes. →Investing Activities: This involves spending the capital that a company receives in productive ways that will help the company to achieve their objectives. These activities can include: buying land, buildings, equipment and other resources that are needed to operate in their business.
→Financing Activities: This activity involves obtaining the adequate funds or capital to begin the operations or to continue operating. The company can obtain capital from creditors (banks; suppliers and owners). They have to repay these creditors and pay a return to the owners. An important function of account is to provide information about the performing measures of the company. This information can show if the managers are achieving the business goals and if the business activities are being well managed. The evaluation and interpretation of financial statements and related performance measures is called Financial analysis.
To make the financial analysis useful the company needs to make sure that it is well aligned with the two major goals of the business (profitability and liquidity). It is important for a business to measure the amount of earnings and cash flows in any given period and whether they are rising or falling, ratios of accounting measures are also very useful tools of financial analysis. Financial and Management Accounting The role of accounting is to assist the decisions makes in an entity. This is done by measuring, processing and communicating financial information that is usually divided into categories of management accounting and financial accounting.
HiLux Chassis Body does NOT cover engine. Toyota RN30 and RN40 Chassis and Body Workshop and Repair Manual. USED - softcover. Get other Toyota. Instant access to available, up-to-date Toyota collision repair technical articles and bulletins, position statements, and repair instructions. Searching for 2012 hilux body repair manual epub book do you really need this book of 2012 hilux body repair manual epub book it takes me 25 hours just to. 2012 hilux body repair manual. Toyota Hilux: repair manual for chassis & body. Toyota repair manual for chassis and body. Toyota Jidōsha Kabushiki Kaisha.
Management Accounting gives information to the internal decision makers, that are charged of achieving the goals of profitability and liquidity. The managers and employees of the financial entity need to get information that tells them how they have been performing and what they can expect in the future. This information can be based on the operating, investing and financial activities of the financial entity. Financial Management this generates reports and communicates them to the external decision makers so that they are able to evaluate in how well the business has been doing and how far the business is in achieving their goals. These reports are called financial statements. Financial Statements report directly on the goals of profitability and liquidity and are used extensively inside and outside of the financial entity to evaluate the success of this financial entity. Users of accounting information Decision makers Management Those with indirect financial interest -Finance Those with direct financial interest - Regulatory Agencies -Marketing -Investors - Labor Unions - Human Resources - Creditors - Investment -Operations and Production - Information System -Tax authorities - Customers - Economic Planners -Accounting Financing the business: obtaining funds so that a company can begin and continue operating Investing resources: Investing assets in productive ways that support a company’s goals.
Producing goods and services: Managing the production of goods and services. Marketing goods and services: Overseeing how goods or services are advertised, sold and distributed. Managing employees: Overseeing the hiring, evaluation, and compensation of employees. Providing information to decision makers: Gathering data about all the aspects of a company’s operations, organizing the data into usable information, and providing reports to managers and appropriate outside parties. Accounting plays a key role in this function. Users with a direct financial interest The accounting information of the company should also be provided to those with a direct financial interest in a business. This people depend on accounting to measure and report information about how this company has been performing.
Many businesses periodically publish a set of general-purpose financial statements that show how far the company is in meeting their company goals of profitability and liquidity. People outside of the company study these financial reports carefully. The two most important groups are investors (including owners) and creditors. Investors are stakeholders who may invest in the business and acquire a part of the ownership in this business. They are usually interested in the past success of the business and its potential earnings. Creditors are those who borrow money or deliver goods to companies before being paid, this can be done in a short and long-term period. The interest of the creditors is usually to see if the company will have enough cash to pay the interest charges and to repay the debt at the appropriate time.
Users with an indirect financial interest Governmental and public groups also have an interest in the financial statements of companies. Users who need accounting information to make decisions in public issues include tax authorities, regulatory agencies and various other groups. Tax authorities companies and individuals pay many kinds of taxes, including federal, state, and city income taxes. For businesses this taxes are mainly decided on the financial statements that they hand in to the tax authorities. Regulatory Agencies most companies must report periodically to one or more regulatory agencies at the federal, state and local levels.
Other groups labour unions study the financial statements of corporations as part of preparing for contract negotiations; a company’s income and costs often play an important role in this negotiations. Accounting Measurement In order to make an accounting measurement the accountant should always have four basic questions in mind: 1.
Chapter 1 Study Guide Accounting
What is measured? When should the measurement be made? What value should be placed on what is measured? How should what is measured be classified? Answering to the first question every system must define what it measures, and accounting is not an exception to this rule.
So basically, financial accounting uses money to gauge the impact of business transactions on separate business entities. Business Transactions Business transactions are economic events that effect the business financial position. There are hundreds or sometimes even thousand different business transaction a day within a company. Transactions can be an exchange of value (purchase, sale, payment, collection or loan) between two or more parties. It can also be an economic event that has the same effect as an exchange transaction but that does not involve an exchange When recorded a business transaction must be related directly to a business entity. Money measure All the transaction in a company are recorded in terms of money. We call this concept money measure.
Money is the only factor that is common within all business transactions, that is the only unit of measure capable of producing financial data that can be compared. Separate Entity For business purposes a business is a separate entity, distinct from their customers, creditors and also its owners.
It should have its own set of financial records and its records and reports should refer only to its own affairs. There are three basic forms of business organizations: Sole partnership, the partnership, the corporation. Accountants recognize each form as an economic unit separate from its owners.
Characteristics of corporations, sole partnerships and partnerships Sole partnership is a business owned by one person. The owner of this type of partnership takes all the profit or losses of the business and is liable for all its obligations. Partnership is like a sole proprietorship in most ways, but the difference is that it has two or more owners. The partners of the company share the profits and losses of the business according to prearranged formula. Owner’s equity is affected by the owner’s investments in and withdrawals from the business and by the business’s revenues and expenses. Simply stated, revenues and expenses are the increases and decreases in owner’s equity that result from operating a business. Generally, a company is successful if its revenues exceed its expenses.
When revenues exceed expenses, the difference is called net income. When expenses exceed revenues, the difference is called net loss. Financial statements are the primary means of communicating important accounting information about a business to those who have an interest in the business.
Income Statement The income statement summarizes the revenues earned and expenses incurred by a business over an accounting period. Many people consider it the most important financial report because it shows whether a business achieved its profitability goal that is, whether it earned acceptable income.
Example of an income statement: Statement of Owners equity The statement of owner’s equity shows the changes in owner’s equity over an accounting period. The balance sheet The purpose of a balance sheet is to show the financial position of a business on a certain date, usually the end of the month or year. It is often called the statement of financial position and it is dated as of a specific date. The balance sheet presents a view of the business as the holder of resouces of assers, that are equal to the claims against those assets.
The claims consist of the company’s liabilities and the owners’s equity in the company. Statement of cash flows The income statement focuces on the company’s profitability and the Statement of cash flows focuses on its liquidity.
Cash flows are the inflows and outflows of cash into and out of a business. Net cash flows are difference between the inflows and outflows. The statement of cash flow is organized according to the three major business activities. Cash flow from operating activities Cash flow from investing activities Cash flow from financing activities The statement of cash flows if related directly to the other three financial statements. Notice that the net income statement comes from the income statement and that withdrawals come from the statement of owners’ equity. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles To ensure that the financial statements are understandable to their users, a set of practices, called generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP), has been developed to provide guidelines for financial accounting.
GAAP and the Independent CPA’s Report Because financial statements are prepared by management and could be falsified for personal gain, all companies that sell shares of their stock to the public and many companies that apply for sizable loans have their financial statements audited by an independent certified public accountant (CPA). An audit is an examination of a company’s financial statements and the accounting systems, controls, and records that produced them. The purpose of the audit is to ascertain that the financial statements have been prepared in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. Organizations that issue accounting standards There are two organisations that issue the accounting standards that are used in the US: The FASB and the IASB.
The financial accounting standards board (FASB) is the most important body for developing rules on accounting practice. This independent body was designed by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) to issue Statements of Financial Accounting Standards. The International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) has approved more than 40 international financial reporting standards (IFRS). Other organizations that influence GAAP The Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (PCAOB), this is a governmental body created by the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, regulates the accounting profession and wide powers to determine the standards that auditors must follow and to discipline them if they do not. The American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA), the professional association of certified public accountants, influences accounting practice through the activities of its senior technical committees. The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), is an agency of the federal government that has the legal power to set and enforce accounting practices for companies whose securities are offered for sale to the general public. As such, it has enormous influence on accounting practice.
The Governmental Accounting Standards Board (GASB), which is under the same governing body as the FASB, issues accounting standards for state and local governments. Professional Conduct The code of professional ethics of the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants governs the conduct of CPAs. The code requires CPAs to act with integrity, objectivity, and independence.
Integrity means the accountant is honest and candid and subordinates personal gain to service and the public trust. Objectivity means the accountant is impartial and intellectually honest. Independence means the accountant avoids all relationships that impair or even appear to impair his or her objectivity. The institute of management accountants (IMA) also has a code of professional conduct. This code emphasizes that management accountants have a responsibility to be competent in their jobs, to keep information confidential except when authorized or legally required to disclose it, to maintain integrity and avoid conflicts of interest, and to communicate information objectively and without bias. Corporate Governance The financial scandals at Enron, World.com and other companies highlighted the importance of corporate governance, which is the oversight of a corporation’s management and ethics by its board of directors.
To strengthen corporate governance, a provision of Sarbanes-Oxley Act requires board of directors to establish an audit committee made up of independent directors who have financial expertise. This provision is aimed at ensuring that boards of directors are objective in evaluating management’s performance. Chapter 2: “Analysing Business Transactions” Measurement Issues Business transactions are economic events that affect the financial position of the company. It is important for a company that the business transaction is recorded at the right time, for this there must be decided when the transaction is occurred (recognition issue). There are three issues corresponding to this, recognition, valuation and classification. When the transaction occurred (recognition issue) What value to place on the transaction (valuation issue) How the components of the transaction should be categorized (the classification issue) Recognition The recognition issue refers to the difficulty that the accountant has of deciding when the business transaction should be recorded. The recognition of this issue is very important, because the date on which the transaction is recorded affects amounts in the financial statements of the company.
According to the accounting tradition, a transaction should always be recorded when the tittle of the merchandise passes from the supplier to the purchaser and creates an obligation to the purchaser to pay this merchandise. The time at which the transaction is recorded is the recognition point. It can be difficult to resolve the recognition issue, for example: in case of an advertising agency that is planning a major advertising campaign for a client. Employees may work on the plan several hours a day for a number of weeks.
They add value to the plan as they develop it. Should this added value be recognized as the plan is being developed or at the time it is completed? Usually, the increase in value is recorded at the time the plan is finished and the client is billed for it. Valuation Valuation issue takes focus on assigning a monetary value to a business transaction and accounting for the assets and liabilities that result from the business transactions. In the general accepted accounting principles it states that all business transactions should be valued at fair value when they occur. Fair value is defined as the exchange of the actual potential business transactions between the market participants.
This practice of recording transactions at exchange price at the point of recognition is commonly referred as the cost principle. It is used because the cost, or exchange price is verifiable. The t-account A good way to start studying the double-entry system is by studying the T-account.
This account has three different parts: a tittle, which describes the asset, liability or owner’s equity account, a left side which is called debit side and a right side which is called credit side. An entry made on the left side of the account is a debit and an entry made on the left side is a credit. “Left” and “Right” are not stated as “inc.